Fish farming management in freshwater involves several key aspects: healthy and robust fingerlings, high-quality ideal fish feed, and proper water and farming management. Not long ago, fish farming was considered a natural activity. However, today, it has become a regulated business like any other.
For Bangladesh’s large population, fish farming plays a crucial role in food security and meeting protein needs by utilizing water bodies efficiently. Proper freshwater fish farming management can create alternative employment opportunities for the unemployed. With increased investment in fish farming, income will grow, leading to financial stability and improving family and social standards.
The natural sources of protein are now in decline. Farming fish in ponds can reduce pressure on these natural resources. Proper management of freshwater fish farming ensures profitable investments.
There is a lot of information available online about freshwater fish farming, often presented separately. This article provides a detailed discussion on freshwater fish farming.
Components of Water in Fish Farming
Having knowledge about the components of water in fish farming is crucial because water quality directly impacts the success of fish farming. Water contains two types of components: dissolved and non-dissolved.
Dissolved Components:
- Gases: Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Hydrogen Sulfide
- Minerals: Calcium, Magnesium, Sodium, Potassium Salts
- Organic Components: Carbohydrates, Proteins, etc.
Non-Dissolved Components:
- Microorganisms:
- Phytoplankton
- Zooplankton
- Non-living substances:
- Minerals: Mud, Silt
- Detritus, Debris, Humus, etc.
Impact of pH in Fish Farming
What is pH?
pH is the measure of acidity and alkalinity. It has no unit but follows a scale from 1 to 14, where 7 is neutral. A pH value below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is alkaline.
Ideal pH for Fish Farming:
The ideal pH for freshwater fish farming is between 7.0 – 8.5, which is slightly alkaline.
Causes of Acidic pH (Below 7):
- Excess feed usage: Uneaten food decomposes, forming organic acids, making the water acidic.
- Accumulation of hydrogen gas in pond sediment.
- Rainwater washing acidic substances (like sulfuric acid) into the pond.
Causes of Alkaline pH (Above 7):
- Decomposed excess food.
- Overgrowth and decay of plankton.
- Excess gases like ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite.
- Overuse of fertilizers or chemicals.
Effect of pH on Fish and Aquatic Life (Swingle, 1969):
| pH Level | Impact |
|---|---|
| 4.0 | Fish die due to acidity. |
| 4.0 – 5.0 | Fish do not reproduce. |
| 4.0 – 6.5 | Fish growth slows down. |
| 6.5 – 9.0 | Optimal growth of fish. |
| 9.0 – 11.0 | Fish growth slows down. |
| 9.5 – 11.0 | Fish do not reproduce. |
| >11.0 | Fish die due to alkalinity. |
Essential Fish Farming Management Practices
- Pre-Stocking Management
- Stocking Management
- Post-Stocking Management
1. Pre-Stocking Management
Before stocking fish, ensure the following:
- Weed and Pond Cleaning:
- Remove aquatic weeds and repair pond banks and bottom.
- Excessive mud at the bottom produces harmful gases.
- Broken pond banks allow unwanted organisms to enter.
- Uneven pond bottoms make harvesting difficult.
- Avoid planting eucalyptus and small-leaved trees near the pond, as their leaves degrade water quality.
- Removal of Predatory Fish:
- Predatory fish like catfish, snakehead, and featherback eat fingerlings and fish feed.
- Methods to remove them:
- Using fine mesh nets.
- Draining and drying the pond.
- Applying Rotenone Powder at 30-40 grams per cubic foot of water.
- Using other chemicals like Phostoxin tablets or T-seed mill (ACI).
Lime Application in Ponds
Benefits of applying lime:
- Maintains pH balance.
- Increases primary productivity by aiding photosynthesis.
- Helps decompose organic waste.
- Improves nutrient availability in water.
- Kills harmful parasites and bacteria.
Lime Application Methods:
- Apply 1 kg lime per decimal on a dry pond bottom.
- If the pond is not dry, dissolve the lime in water before application.
- Allow 3-4 days before refilling the pond with water.
Precautions:
- Apply lime against the wind direction.
- Do not pour water into the lime; instead, mix lime into the water.
- Avoid using plastic containers.
- Wear a mask or cloth to cover your nose and mouth.
2. Stocking Management
- Species Selection Based on Water Layer:
| Water Layer | Fish Species |
|---|---|
| Surface | Silver Carp, Catla, Bighead |
| Middle | Rohu |
| Bottom | Mrigal, Carp, Bata |
| All Layers | Tilapia, Punti, Pangas |
- Stocking Density:
| Fish Species | Size | Stocking Density (per decimal) |
|---|---|---|
| Pangas | 5-7 inches | 100-150 |
| Silver Carp | 5-7 inches | 3-15 |
| Bighead Carp | 5-7 inches | 2-3 |
| Catla | 5-6 inches | 1-3 |
| Rohu | 5-6 inches | 2-5 |
| Mrigal/Kalbaush | 5-6 inches | 2-5 |
| Common Carp | 3-4 inches | 1-5 |
| Bata | 2-3 inches | 1-3 |
| Tilapia | 2-3 inches | 12-250 |
- Healthy Fingerlings Identification:
- Bright, shiny, and slippery body.
- Active movement.
- Swims against the current.
- Flicks head when tail is squeezed.
- Fingerling Transport & Acclimatization:
- Ensure oxygen supply during transport.
- Acclimatize by floating the transport bag in pond water.
3. Post-Stocking Management
- Monthly application of 200g lime per decimal.
- Apply fertilizers based on natural feed availability:
- 100g urea + 50g TSP per decimal per week if natural feed is low.
- Introduce supplementary feed for faster growth.
Tilapia Feeding Chart:
| Days | Weight | Feed Type | Daily Feed % of Body Weight | Feed Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-15 | 5-15g | Starter (Crumbles) | 15-20% | 3 times |
| 16-30 | 15-40g | Starter (Pellets) | 8-10% | 3 times |
| 31-60 | 40-100g | Grower | 5-7% | 2 times |
| 61-100 | 100g+ | Finisher | 2-3% | 2 times |
Supplementary Feeding
Considerations for Supplementary Feeding:
- Adjust feeding levels based on fish survival rate, growth, and feeding behavior.
- Every seven days, catch a few fish to monitor their growth and health.
- Reduce feed quantity appropriately during winter.
- If grass carp and sarpunti are present, provide green grass and soft leaves.
- Keep one day a week feed-free for better fish health.
- Avoid feeding during rainy weather.
Fish Health and Growth Examination:
- Periodically drag a net through the pond to observe fish health, growth, and any signs of disease.
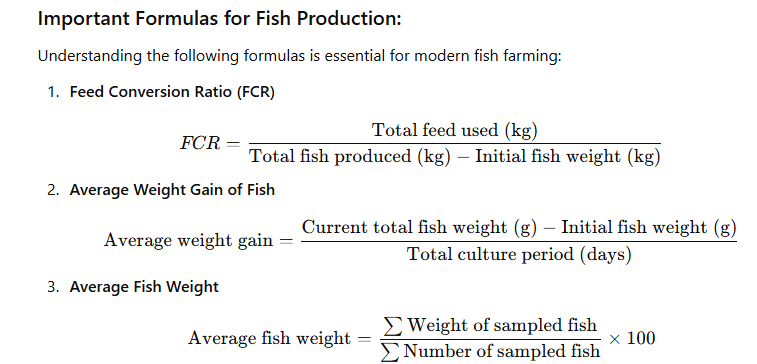
Important Formulas for Fish Production:
Fish Harvesting:
Since not all fish grow at the same rate, consider the following before harvesting:
- Fish weight – Ensure the fish are of marketable size.
- Market price – Fish prices tend to be higher during Ramadan, Puja, and wedding seasons.
- Risks – Rainy seasons, drought, winter, and theft pose risks to fish farming.
- Availability of fingerlings – Ensure restocking after harvesting.
Methods of Harvesting:
-
Partial Harvesting & Restocking:
- Harvest 10-15% of fish and restock accordingly.
-
Complete Harvesting:
- Harvest all fish, though in large water bodies, complete harvesting may not always be feasible.
Fish Marketing:
Live fish fetch higher market prices. Consider the following for effective fish marketing:
- Handle fish carefully during harvesting. Stress can cause fish to spoil quickly.
- Deliver fish to the market as early as possible for better sales.
- Transport fish either alive or preserved in ice.